Need A Commercial Photographer?
Looking for photography for your business, real estate, or commercial products? RMDP360MEDIA provides commercial photography and video.
Managing Your Aerial Media
Document your commercial building project using drone video technology for mapping, aerial video, progress images, & point of interest. An aerial perspective helps managers perceive the project all along the way.
4K video and maps to help create spectacular marketing videos and 2D maps for commercial business

COMMERCIAL PHOTOGRAPHY
We add value to your commercial business or organization by providing high quality product images, head shots, documentary, and real estate photos
Premium services and products
PROFESSIONAL WEBSITES
Whether your project is large or small, your message is what is important. You work hard to offer great products & services, your website should resemble that hard work!
WordPress Website Experts

HD VIDEO PRODUCTION
Your business needs to get it’s message out and what better way than a video that tells your story and engages visitors with promotionals and documentaries.
YouTube media specialists

SOCIAL MEDIA SERVICES
Every business needs to be using social media the right way. Our team will bring new life to your online presence and build a following you can market to.
Perception is reality on the web
Aerial Digital and Legacy Content
Here is what RMDP360MEDIA can provide for your next project.
Our Customers Love Us
Don’t Just Take Our Word For It, Read It From Them
Flexible Pricing Plans
We Have Pricing Plans To Suit Every Website Need
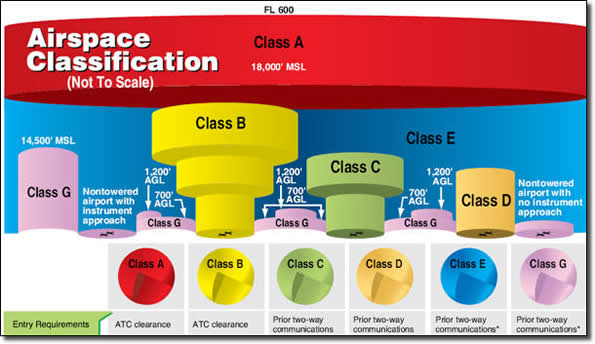
Class E or G Airspace
$399
Up to 25 still images
2 minutes of 1080 HD video
High level and low-level flights up to 400′
.jpg or .png image files
.mov video files
Class C & D Airspace
$469
Airspace Flight Approval
21-40 Still Images
2 Minutes 1080 HD Video
24 Hour Turnaround
.jpg or .png files
.mov video
Class B Airspace
$499
Airspace Flight Approval
72 Hour Notice
Minimum 40 RAW Images
5 minutes of 4K Video
Same Day Turnaround
.mov, .wmv, .mp4 video
Airspace Restrictions
There are many types of airspace restrictions in the United States.
Below is a list of restrictions that commonly affect UAS flights, including:
Stadiums and Sporting Events
Near Airports
Security Sensitive Airspace Restrictions
Restricted or Special Use Airspace
Washington, DC
Emergency and Rescue Operations
The FAA prohibits flying our drones over any emergency or rescue operations including:
Wildfires
Hurricanes